Examples
HANDS-ON USECASE EXAMPLES
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Hugging Face Trainer | Train LLaMA 3-8B ~20% faster with over 40% memory reduction on Alpaca dataset using 4 A100s with FSDP |
| Lightning Trainer | Increase 15% throughput and reduce memory usage by 40% with LLaMA3-8B on MMLU dataset using 8 A100s with DeepSpeed ZeRO3 |
| Medusa Multi-head LLM (Retraining Phase) | Reduce memory usage by 80% with 5 LM heads and improve throughput by 40% using 8 A100s with FSDP |
| Vision-Language Model SFT | Finetune Qwen2-VL on image-text data using 4 A100s with FSDP |
| Liger ORPO Trainer | Align Llama 3.2 using Liger ORPO Trainer with FSDP with 50% memory reduction |
HuggingFace Trainer¶
How to Run¶
Locally on a GPU machine¶
You can run the example locally on a GPU machine. The default hyperparameters and configurations work on single node with 4xA100 80GB GPUs and FSDP.
Example
Remotely on Modal¶
If you do not have access to a GPU machine, you can run the example on Modal. Modal is a serverless platform that allows you to run your code on a remote GPU machine. You can sign up for a free account at Modal.
Example
pip install modal
modal setup # authenticate with Modal
modal run launch_on_modal.py --script "run_qwen2_vl.sh"
Notes
-
This example uses an optional
use_ligerflag. If true, it does a 1 line monkey patch to apply liger kernel. -
The example uses Llama3 model that requires community license agreement and HuggingFace Hub login. If you want to use Llama3 in this example, please make sure you have done the following:
- Agree on the community license agreement .
- Run
huggingface-cli loginand enter your HuggingFace token.
-
The default hyperparameters and configurations work on single node with 4xA100 80GB GPUs. For running on device with less GPU RAM, please consider reducing the per-GPU batch size and/or enable
CPUOffloadin FSDP.
Benchmark Result¶
Llama¶
Info
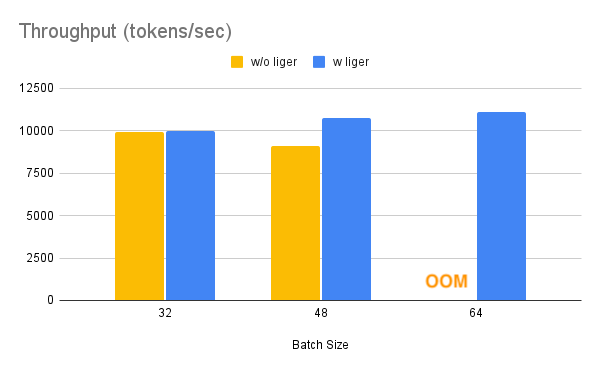
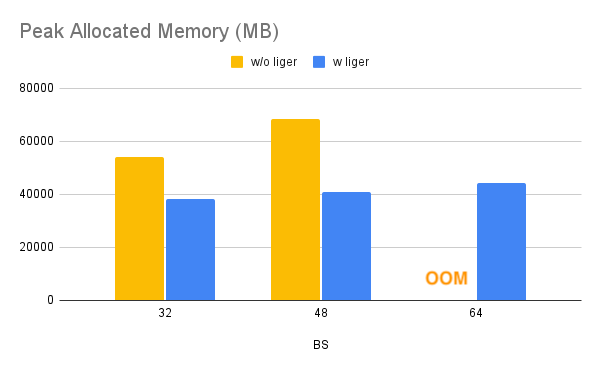
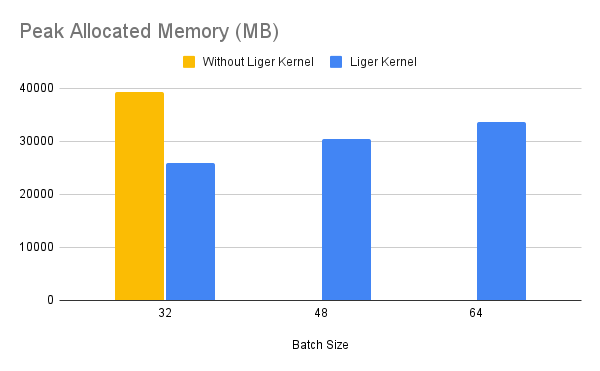
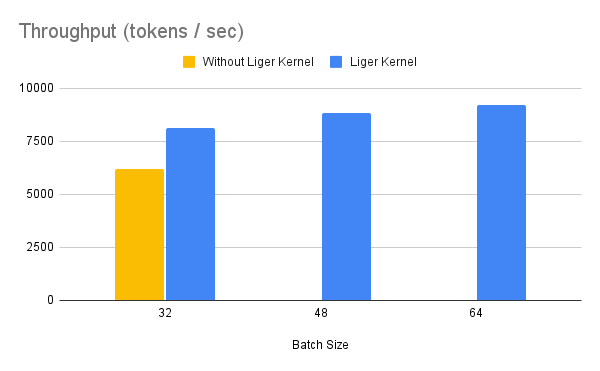
Benchmark conditions: Model= LLaMA 3-8B,Datset= Alpaca, Max seq len = 512, Data Type = bf16, Optimizer = AdamW, Gradient Checkpointing = True, Distributed Strategy = FSDP1 on 4 A100s.
Throughput improves by around 20%, while GPU memory usage drops by 40%. This allows you to train the model on smaller GPUs, use larger batch sizes, or handle longer sequence lengths without incurring additional costs.
Qwen¶
Info
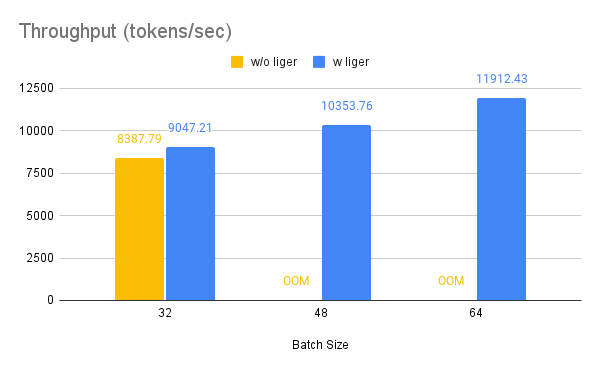
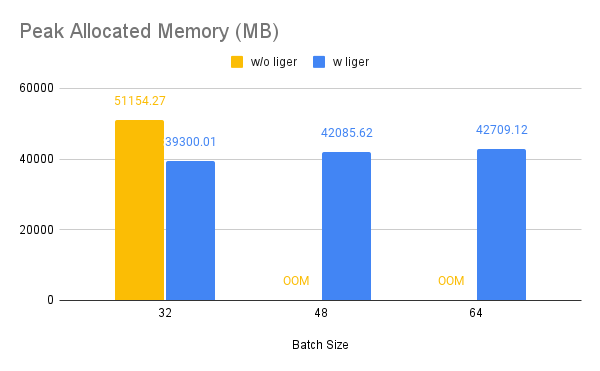
Benchmark conditions: Model= Qwen2-7B, Dataset= Alpaca, Max seq len = 512, Data Type = bf16, Optimizer = AdamW, Gradient Checkpointing = True, Distributed Strategy = FSDP1 on 4 A100s.
Throughput improves by around 10%, while GPU memory usage drops by 50%.
Gemma 7B¶
Info
Benchmark conditions: Model= Gemma-7B, Dataset= Alpaca, Max seq len = 512, Data Type = bf16, Optimizer = AdamW, Gradient Checkpointing = True, Distributed Strategy = FSDP1 on 4 A100s.
Throughput improves by around 24%, while GPU memory usage drops by 33%.
Lightning Trainer¶
How to Run¶
Locally on a GPU machine¶
You can run the example locally on a GPU machine.
Example
pip install -r requirements.txt
# For single L40 48GB GPU
python training.py --model Qwen/Qwen2-0.5B-Instruct --num_gpu 1 --max_length 1024
# For 8XA100 40GB
python training.py --model meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B --strategy deepspeed
Notes
-
The example uses Llama3 model that requires community license agreement and HuggingFace Hub login. If you want to use Llama3 in this example, please make sure you have done the following:
- Agree on the community license agreement
- Run
huggingface-cli loginand enter your HuggingFace token.
-
The default hyperparameters and configurations for gemma works on single L40 48GB GPU and config for llama work on single node with 8xA100 40GB GPUs. For running on device with less GPU RAM, please consider reducing the per-GPU batch size and/or enable
CPUOffloadin FSDP.
Medusa¶
Medusa is a simple framework that democratizes the acceleration techniques for LLM generation with multiple decoding heads. To know more, you can check out the repo and the paper .
The Liger fused CE kernel is highly effective in this scenario, eliminating the need to materialize logits for each head, which usually consumes a large volume of memory due to the extensive vocabulary size (e.g., for LLaMA-3, the vocabulary size is 128k).
The introduction of multiple heads can easily lead to OOM (Out of Memory) issues. However, thanks to the efficient Liger fused CE, which calculates the gradient in place and doesn't materialize the logits, we have observed very effective results. This efficiency opens up more opportunities for multi-token prediction research and development.
How to Run¶
Example
git clone git@github.com:linkedin/Liger-Kernel.git
cd {PATH_TO_Liger-Kernel}/Liger-Kernel/
pip install -e .
cd {PATH_TO_Liger-Kernel}/Liger-Kernel/examples/medusa
pip install -r requirements.txt
sh scripts/llama3_8b_medusa.sh
Notes
-
This example uses an optional
use_ligerflag. If true, it does a monkey patch to apply liger kernel with medusa heads. -
The example uses Llama3 model that requires community license agreement and HuggingFace Hub login. If you want to use Llama3 in this example, please make sure you have done the followings:
- Agree on the community license agreement https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B
- Run
huggingface-cli loginand enter your HuggingFace token
-
The default hyperparameters and configurations work on single node with 8xA100 GPUs. For running on device with less GPU RAM, please consider reducing the per-GPU batch size and/or enable
CPUOffloadin FSDP. -
We are using a smaller sample of shared GPT data primarily to benchmark performance. The example requires hyperparameter tuning and dataset selection to work effectively, also ensuring the dataset has the same distribution as the LLaMA pretraining data. Welcome contribution to enhance the example code.
Benchmark Result¶
Info
- Benchmark conditions: LLaMA 3-8B, Batch Size = 6, Data Type = bf16, Optimizer = AdamW, Gradient Checkpointing = True, Distributed Strategy = FSDP1 on 8 A100s.
Stage 1¶
Stage 1 refers to Medusa-1 where the backbone model is frozen and only weights of LLM heads are updated.
Warning
num_head = 3¶


num_head = 5¶


Stage 2¶
Warning
Stage 2 refers to Medusa-2 where all the model weights are updated including the backbone model and llm heads.
num_head = 3¶


num_head = 5¶


Vision-Language Model SFT¶
How to Run¶
Locally on a GPU Machine¶
You can run the example locally on a GPU machine. The default hyperparameters and configurations work on single node with 4xA100 80GB GPUs.
Example
#!/bin/bash
torchrun --nnodes=1 --nproc-per-node=4 training_multimodal.py \
--model_name "Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct" \
--bf16 \
--num_train_epochs 1 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 8 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 8 \
--eval_strategy "no" \
--save_strategy "no" \
--learning_rate 6e-6 \
--weight_decay 0.05 \
--warmup_ratio 0.1 \
--lr_scheduler_type "cosine" \
--logging_steps 1 \
--include_num_input_tokens_seen \
--report_to none \
--fsdp "full_shard auto_wrap" \
--fsdp_config config/fsdp_config.json \
--seed 42 \
--use_liger True \
--output_dir multimodal_finetuning
ORPO Trainer¶
How to Run¶
Locally on a GPU Machine¶
You can run the example locally on a GPU machine and FSDP.
Example
import torch
from datasets import load_dataset
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
from trl import ORPOConfig # noqa: F401
from liger_kernel.transformers.trainer import LigerORPOTrainer # noqa: F401
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct",
dtype=torch.bfloat16,
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
"meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct",
max_length=512,
padding="max_length",
)
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
train_dataset = load_dataset("trl-lib/tldr-preference", split="train")
training_args = ORPOConfig(
output_dir="Llama3.2_1B_Instruct",
beta=0.1,
max_length=128,
per_device_train_batch_size=32,
max_steps=100,
save_strategy="no",
)
trainer = LigerORPOTrainer(
model=model, args=training_args, tokenizer=tokenizer, train_dataset=train_dataset
)
trainer.train()